Configuration Registers
This module contains the building blocks of the configuration registers tree. Four modules are defined:
reg_ro.vhd: Implements a read-only register.reg_rw.vhd: Implements a register that can be read and written.reg_mux.vhd: Contains a multiplexer that can switch the control signals to multiple registers.reg_demux.vhd: Complementary to the mux, can switch the outputs of the register to one common signal.
All these modules use two types of records to simplify connections, both defined in the globals package: Here
reg_ro
Ports:
clk_fpga_i: Input clock.rst_i: Input synchronous reset.config_reg_i: Input of a typeconfig_register_in_t.config_reg_o: Output of a typeconfig_register_out_t.data_i: This port is sampled at each clock and saved into the internal register.data_o: Mirrors the content of the internal register.
This module is going to be used mainly to read status values generated from other modules. For example, error bits, status bits, or values.
reg_rw
Generic:
DATA_INIT: This value will be set when reset is active.
Ports:
clk_fpga_i: Input clock.rst_i: Input synchronous reset.config_reg_i: Input of a typeconfig_register_in_t.config_reg_o: Output of a typeconfig_register_out_t.data_o: Mirrors the content of the internal register.
This module is going to be used mainly to control other modules’ behavior. A default state can be specified with the DATA_INIT generic.
reg_mux
Generic:
OUTPUTS_N: Sets the number of outputs. The default value is 8.
Ports:
clk_fpga_i: Input clock.rst_i: Input synchronous reset.addr_i: Controls to which output the input signal is propagated.regs_i: Input of a typeconfig_register_in_t.regs_o: A vector ofconfig_register_out_t.
This multiplexer is a synchronous design; the input is registered, and it’s going to be available on the output with one clock cycle of delay. This is done to accommodate deep registers trees where signal propagation times can be a problem.
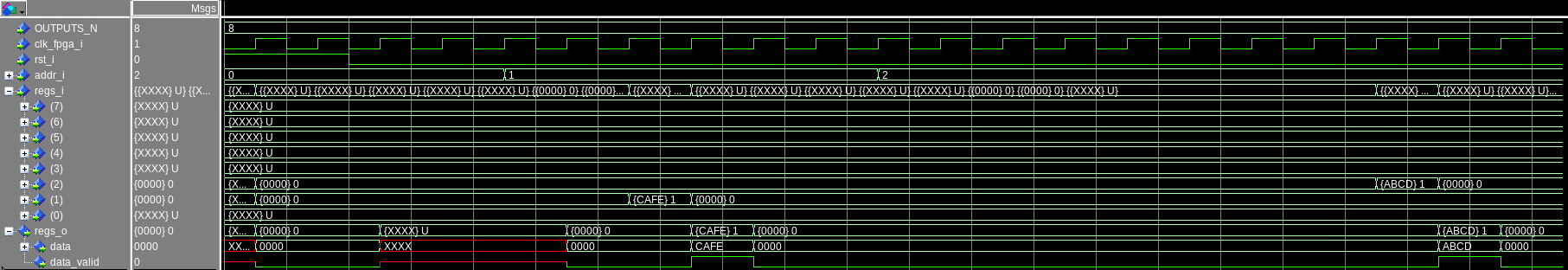
reg_demux
Generic:
OUTPUTS_N: Sets the number of outputs. The default value is 8.
Ports:
clk_fpga_i: Input clock.rst_i: Input synchronous reset.addr_i: Controls to which output the input signal is propagated.regs_i: A vector ofconfig_register_in_t.regs_o: Output of a typeconfig_register_out_t.
The behavior of this module is the same as the multiplexer.
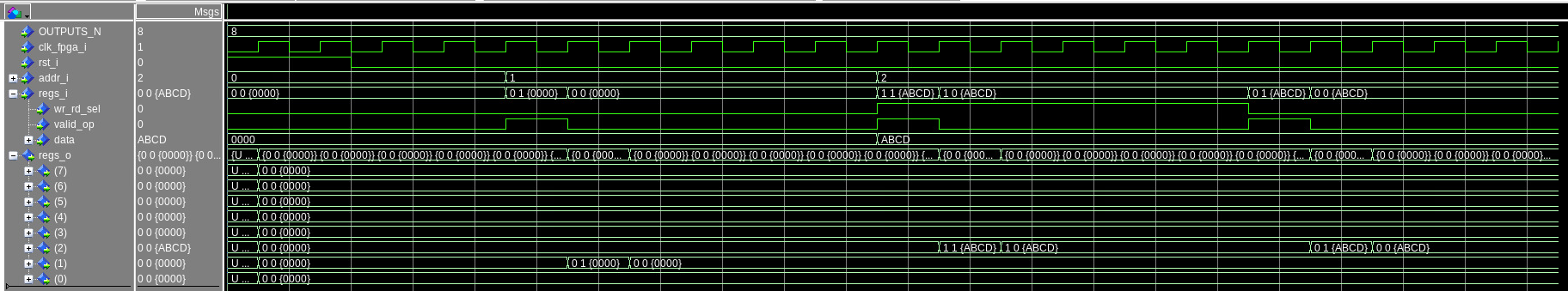
Example
An example of the usage can be seen in the testbench.
Additional Notes
The waveforms show a reset signal not synchronous. However, this doesn’t change the module behavior.