HotRIO master tx
This module generates the HotRIO packets as defined in the HotRIO protocol. The interface with the PCS is 8 bits.
This module must be clocked with the transmission clock provided by the PCS.
This module takes in input HotRIO packets as defined in the globals package. The sent_o signal is pulsed high for one clock cycle when the packet to be sent has been latched internally.
The HOTRIO_PCS_FREQUENCY generic is used to generate the timing flags, its value, in MHz must match the frequency of the used clock.
Generics
Name |
Description |
Default value |
|---|---|---|
HOTRIO_PCS_FREQUENCY |
The frequency (in MHz) at which the packets are sent to the PCS. Used to calculate the number of clock cycles for the markers |
125 |
Ports
Name |
Mode |
Description |
Type |
|---|---|---|---|
clk_i |
IN |
Input clock signal, must be connected to the TX clock of the PCS |
std_logic |
rstn_i |
IN |
Active-low reset signal, synchronized to the internal clock internally |
std_logic |
hotrio_packet |
IN |
Contains the HotRIO packet to be transmitted |
hotrio_packet_t* |
tx_pcs_data_o |
OUT |
Output PCS data |
std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) |
tx_pcs_kchar_o |
OUT |
Output k-character flag |
std_logic |
sent_o |
OUT |
Flag that indicates that the packet has been sent |
std_logic |
pulse_2us |
OUT |
Pulse that signals that a “2us” marker has been sent |
std_logic |
pulse_1ms |
OUT |
Pulse that signals that a “1ms” marker has been sent |
std_logic |
pulse_1s |
OUT |
Pulse that signals that a “1s” marker has been sent |
std_logic |
* Defined in the Globals package
Dependencies
Name |
Motivation |
|---|---|
Types definition and HotRIO constants |
|
Used to synchronize the reset signal to the internal clock domain |
Implementation details
This module is divided in three parts. The first is the state machine that generates the HotRIO packets. The second is the logic that generates the k-character flags, inserting the markers for the 2us, 1ms and 1s. The third part generates the parity bits of the HotRIO packet.
State machine
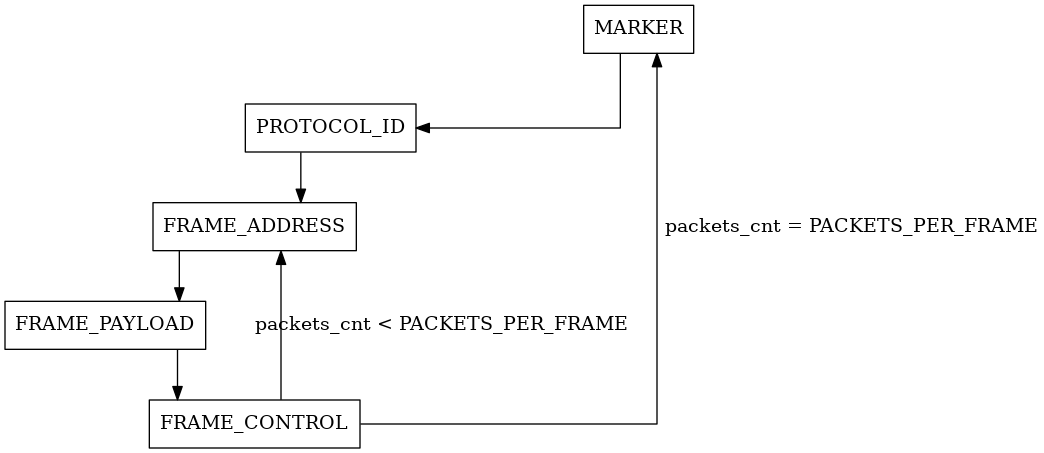
The state machine consists on five states: MARKER, PROTOCOL_ID, FRAME_ADDRESS, FRAME_PAYLOAD and FRAME_CONTROL.
As this module is the transmission side of a master, there is no synchronization with external signals and the state machine starts as soon as the reset signal is de-asserted.
The MARKER state is used to send the special characters to the PCS. The marker to be sent is selected by the marker generation part of this module. In this state, the k-character flag to the PCS is asserted to signal that the current byte is a special character.
The PROTOCOL_ID state sends the protocol ID of the HotRIO protocol to the PCS. The protocol ID is defined in the globals package. During this state, the latched and further changes in the hotrio_packet input are ignored.
The FRAME_ADDRESS state sends the address of the frame to the PCS.
In the FRAME_PAYLOAD state, the payload is sent, starting from the highest byte to the lowest. This is implemented with a simple shift register. A counter is used to keep track of the current byte being sent. The length of the payload is defined in the global package as HOTRIO_BYTES_IN_PAYLOAD.
The last state is the FRAME_CONTROL. In this state, the control byte is sent to the PCS. A counter is used to keep track of the number of HotRIO packets to be sent in one frame. This is defined in the global package as PACKETS_PER_FRAME. Also in this state, the input hotrio_packet is latched to be sent in the next packet.
Marker generation
During instantiation, the module calculates the number of HotRIO frames that will be sent in a 2 microseconds slot. This is done with the following formula: FRAMES_IN_2MICRO = 2 * HOTRIO_PCS_FREQUENCY / BYTES_PER_FRAME. Where BYTES_PER_FRAME is defined in the globals package and contains the number of bytes in an HotRIO packet.
The rest of the implementation consists of three cascading counters, one for each marker.
Parity bits generation
The parity bits are generated by an instance of the parity_gen module. The calculation is done byte-by-byte during transmission. The process byte_select uses the state machine status to select the byte to be sent to the parity generator.